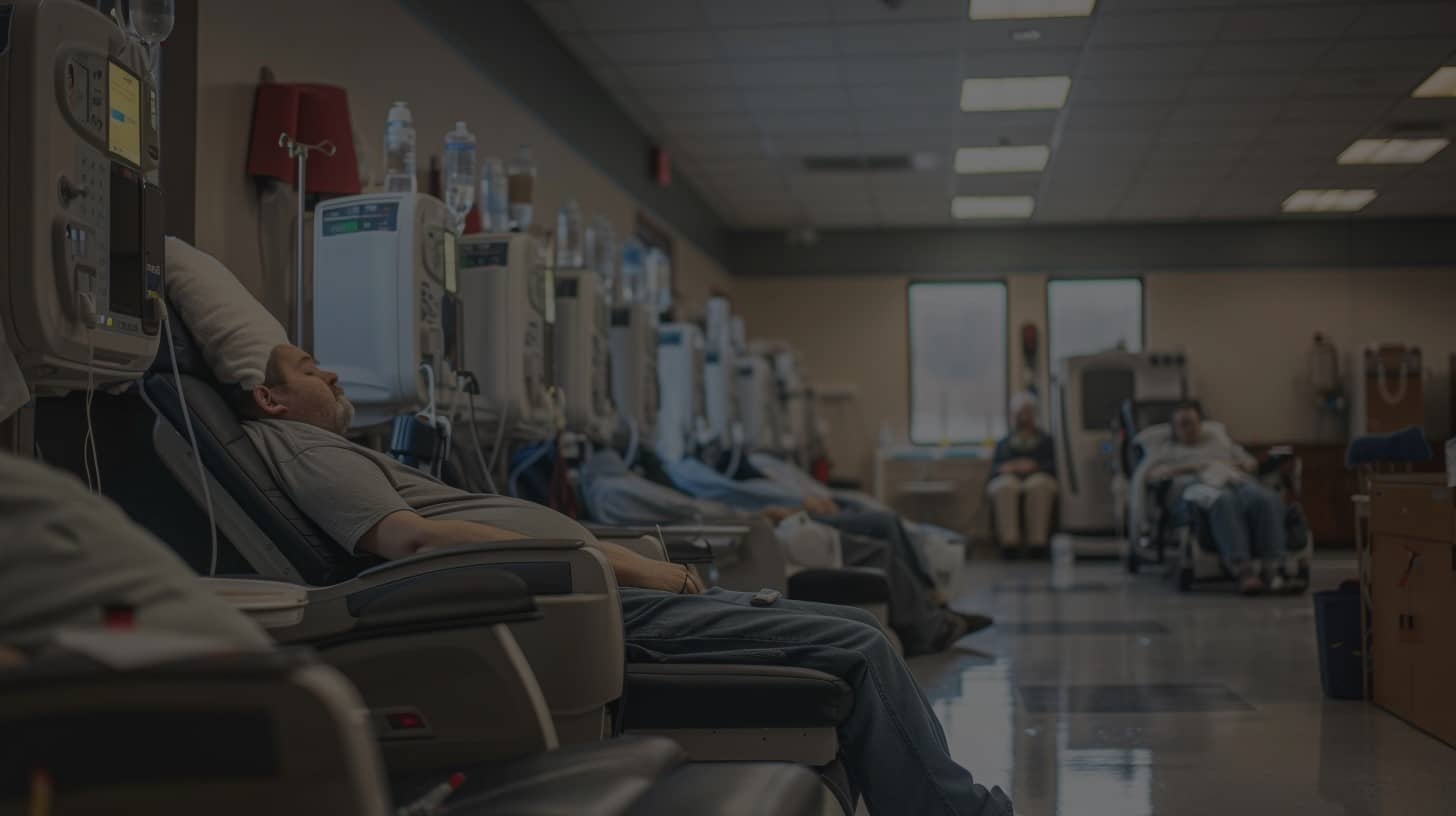

How Do Dialysis Patients Die? Dialysis, a life-saving medical procedure replaces renal functions of dysfunctional kidneys by eliminating metabolic waste and excessive fluids from the blood. This life-saving treatment is critical for patients with End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD). However, it no more cures your kidney failure than curing cholesterol prevents a heart attack; you will remain at risk for near infinite downstream complications some of which death can result. Understanding these hazards and the major causes of death in dialysis patients is important to enhance clinical practices, as well as patient outcomes. They will soon learn, How Do Dialysis Patients Die.

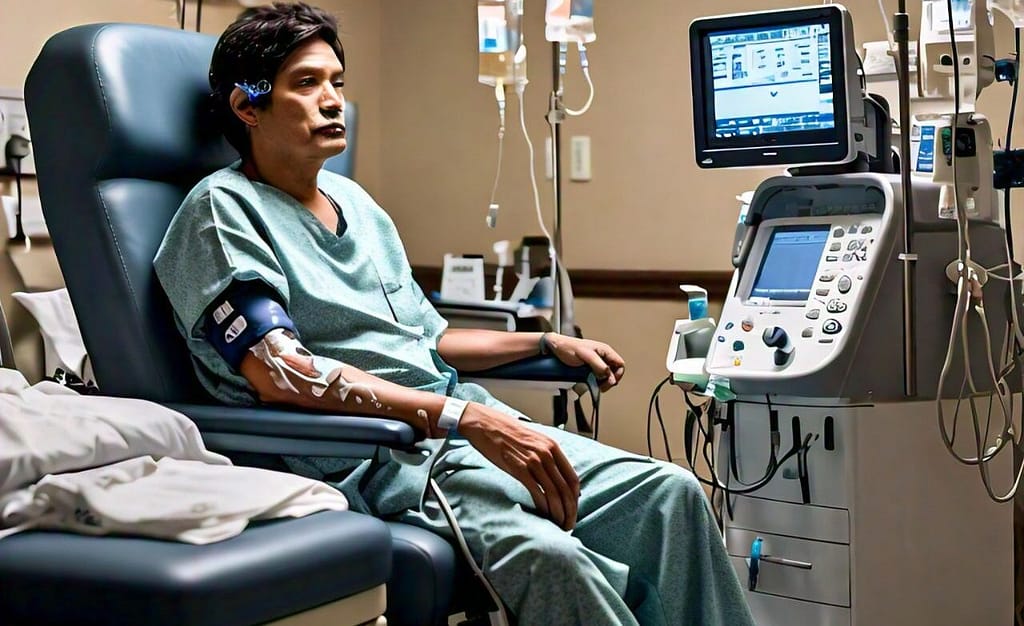
Cardiovascular diseases are the most common cause of death in dialysis recipients. The cardiovascular system is under great tension caused by volume overload, hypertension, and other kidney failure-associated variables which raise the risk for myocardial infarctions (MI), cerebrovascular accident Memory card( CVA) as well as cardiac failure.
Hypertension: High blood pressure is common among those suffering from renal failure and this may worsen cardiovascular events.
Fluid Overload: If too much fluid has not been removed during dialysis, this contributes to volume overload and increases the heart’s workload.
Electrolyte Imbalances: If there are variations in potassium, calcium, and phosphorous levels it can lead to arrhythmias also cause other cardiac disturbances.
This type of infection is a major complication in dialysis patients, who are uniquely predisposed to infections because they have repeated vascular access and compromised immune systems. Local infections (eg, dialysis access site) or systemic infection (eg. sepsis).
Access Site Infections: Infection can develop at the catheter or fistula site.
Peritonitis: Peritoneal infection (peritonitis) during peritoneal dialysis poses a significant risk.
Bloodstream Infections: Bacteria can enter the bloodstream through the dialysis process, causing severe infections.
While dialysis is a life-saving procedure, it can also cause potentially fatal complications.
You should also visit: Kidney Transplant Recovery: A Step-by-Step Guide
Hypotension: A sudden drop in blood pressure during dialysis can lead to stroke and organ damage.
Cardiac Arrhythmias: Rapid changes in electrolyte levels during dialysis can trigger catastrophic arrhythmias.
Dialysis Disequilibrium Syndrome: This rare condition causes seizures, coma, and other neurological symptoms due to rapid changes in fluid and electrolytes.
Malnutrition is common in dialysis patients due to dietary restrictions and protein requirements. This leads to tissue damage, a weakened immune system, and an increased risk of infection and other complications.
Chronic kidney disease often leads to anemia, which can worsen heart disease and lower the immune system.
Dialysis patients often struggle with other chronic diseases, such as diabetes, which can complicate their health and increase their risk of death.
Control of hypertension: intensive medication-based hypertension and lifestyle modification.
Fluid Management: Monitoring and monitoring fluid intake and excretion during dialysis.
Electrolyte Monitoring: Routine blood tests to monitor and adjust electrolyte levels.
Hygiene measures: Adhere to strict hygiene and aseptic procedures during dialysis to prevent infection.
Routine check-ups: frequent monitoring for symptoms of infection and prompt antibiotic therapy upon diagnosis.
Vaccination: Ensuring that patients are aware of vaccinations, especially for influenza and pneumococcal disease.
Dietary advice: To provide customized dietary guidelines to ensure adequate nutrition while following a kidney-friendly diet.
Nutrition: The use of supplements as needed to prevent malnutrition and promote overall health.
A comprehensive view
Multidisciplinary approach: A variety of healthcare professionals including allergists, dietitians, and social workers were involved in providing comprehensive care.
Patient education: Educating patients and their families about the risks associated with dialysis and strategies to effectively manage these risks.
While dialysis is mandatory for individuals with ESRD, there are major risks. The major causes of death in dialysis patients are cardiovascular disease, infections, and complications related to dialysis. We want you to know, how dialysis patients die. By understanding these risk factors and establishing preventive strategies, healthcare providers can improve injection patients’ quality of life and outcomes. Continued assessment and patient education are critical in addressing and reducing dialysis-related risks to ensure patients receive optimal care.
Can Allergies Make You Cough? Allergy is one of the most widespread diseases or conditions…
Which Vitamin Deficiency Results in Hair Loss? This is a problem that people of all…
Can Gas Cause Back Pain? Sometimes, it is not easy to determine the cause of the…
Can Muscle Knots Cause Wrist Pain? Some of the main causes of pain include muscles…
Can You Drink Alcohol While Taking Steroids? This question of alcohol consumption and steroids is…
Can Allergies Make You Cough? Coughing is a normal physiological response that makes use of…