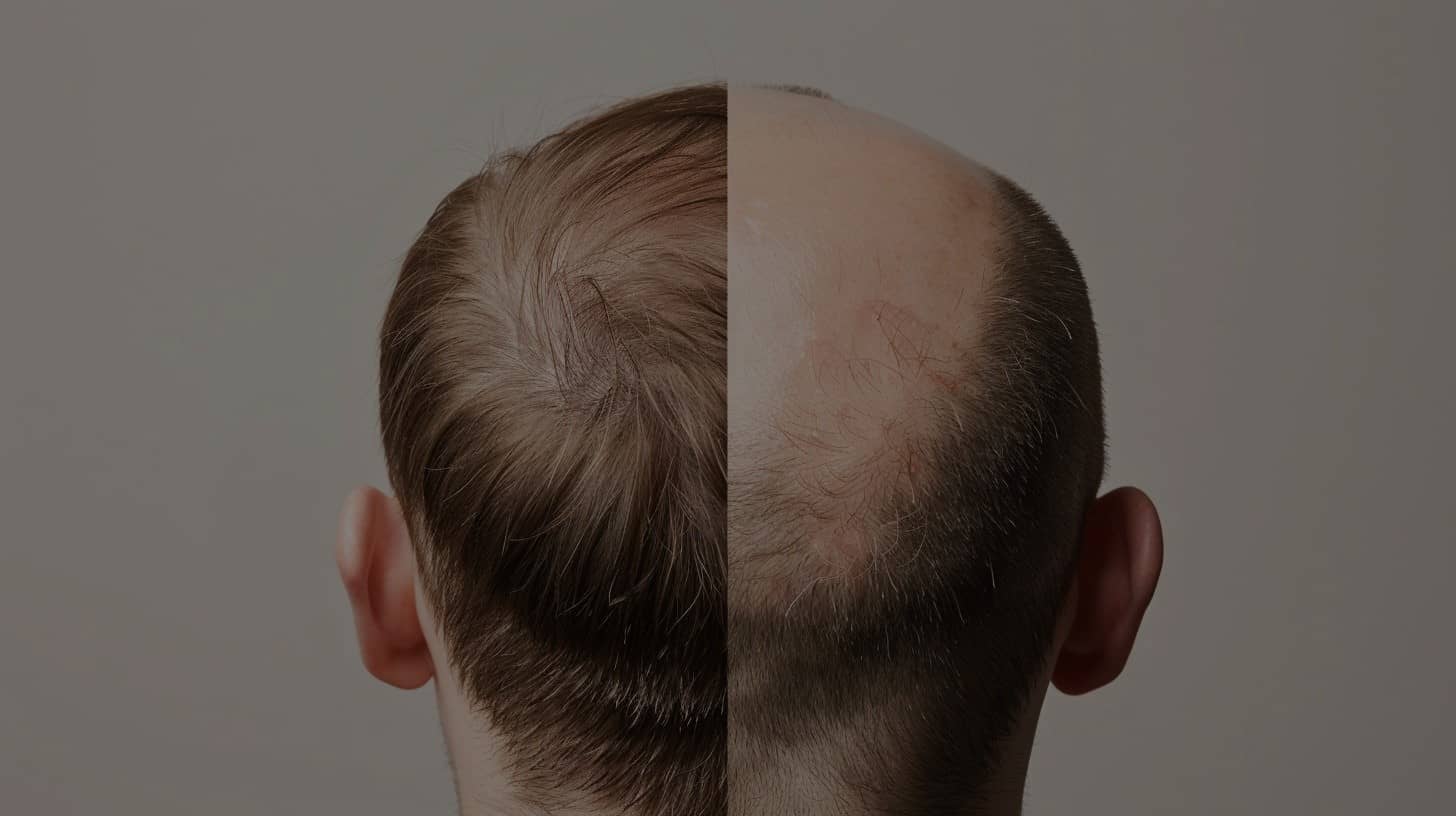
Hair Shedding vs. Hair Loss, human hair is a lot more complex than skin cells; the curled strands that beautify the exterior surface of the head are as important as the interior strands that make up the personality of an individual. When one wakes up in the morning or touches their hair only to find that there are more hairs on the pillow or in the comb than before, or the hair simply appears thinner, it incites alarms. However, one has to differentiate between hair shedding and hair loss.
Hair shedding is widely recognized as a normal process in the life cycle of the hair. A person can lose between 50 to 100 hairs daily and this is very normal. This form of shedding arises from the hair’s progression through its various phases: Anagen phase (growth phase), catagen phase (transition phase), and telogen phase (actively resting phase). Such hairs that are shed in this stage are usually replaced by the new hairs that are growing.
To grasp the concept of hair shedding, one must first understand the hair growth cycle. To grasp the concept of hair shedding, you should first understand the hair growth cycle:
1. Anagen Phase: This phase is known to be of active growth and new hair is produced from the hair follicles. The anagen phase, where the hair grows, can take as long as seven years and may take only two this is because hair has two different types of growth rates.
2. Catagen Phase: A short and intermediate phase that means the non-growth in its active sense. Seventy to one hundred twenty-five small ‘bullets’ of hair root are broken and released from the dermal papilla; hairs become microscopically shorter; it lasts for two to three weeks.
3. Telogen Phase: In this phase hair that is on the scalp sheds off while at the base of the follicle, a new hair begins to develop and the follicle begins a new cycle of anagen phase after approximately ninety days.
Hair shedding, unlike hair loss, means that the situation is even worse and much more serious, which in most cases are lifelong condition. Such a condition may be a result of; genetic factors, disease, or any other reason. Hair loss always warrants a medical examination to have the cause of the hair loss evaluated and the management of the hair loss done under the patient’s circumstances.
Several factors contribute to hair loss, including The causes for hair loss include:
1. Genetic Factors (Androgenetic Alopecia): Also referred to as androgenetic alopecia is the most common form of hair loss disease that is based on genetic and hormonal factors and in these it can be classified into male and female.
2. Medical Conditions: Some diseases alopecia areata, thyroid disease, and lupus; are among those diseases that will lead to hair loss once the affected subject contracts them.
3. Pharmaceuticals and Treatments: Some of the drugs that may lead to hair loss include cancer treatment drugs, arthritis, anti-depression, and cardiovascular drugs.
4. Stress and Trauma: Despite physical pressure and emotional stress that are commonly implicated in causing the condition, it goes by the name of telogen effluvium.
5. Nutritional Deficiencies: A lack of essential nutrients, such as iron, vitamin D, and proteins, can compromise hair strength and lead to loss.
You should also visit: Can Hypertension Cause Dehydration?
– Hair Shedding: A transient phenomenon, part of the hair’s natural cycle, with regrowth typically occurring without medical intervention.
– Hair Loss: Often progressive and potentially permanent, depending on the etiology. Medical treatment may be required to stimulate regrowth or manage the condition.
– Hair Shedding: A minor rise in hair loss that occurs over the sink, in pillows, in the shower, or in a comb, with minor changes in hair volume density.
– Hair Loss: Significant signs of MPB would include receding hairlines, spots of baldness, or general thinning of hair all over the head.
– Hair Shedding: Usually attributed to the natural hair growing pattern, stress, or fluctuation in hormones for some time.
– Hair Loss: This in most cases may be a result of some inherited genes, hormonal fluctuations, diseases, or other persistent causes.
Addressing hair shedding involves promoting overall hair health and mitigating potential triggers:
1. Nutritional Maintenance: Frequent washing and damaging of hair should be avoided and one should ensure that one’s diet is rich in the nutrients necessary for hair growth.
2. Stress Management: Include practices like performing yoga, meditation, and exercise to reduce the effects of stress on the hair.
3. Gentle Hair Care: Use gentle shampoos whenever possible and do not fry the hair with either a straightener or a curling iron, pull it into tight ponytails, or use chemicals that can contribute to the shedding.
4. Scalp Care Routine: Contributing to the promotion of blood supply and improving the outcome of hair growth, it is recommended to make frequent scalp massages.
When hair loss is likely to be other than shedding, it is advisable to visit a health care provider. General treatment options include:
1. Medications: Minoxidil and finasteride are the only two medications known to slow down the progression of hair loss and in some instances encourage hair regrowth.
2. Laser Therapy: Low-level laser therapy or LLLT is an endeavor with less intercession that can stimulate healing and hair regeneration.
3. Hair Transplantation: Depending on the situation, there might be the need to undergo surgery such as a hair transplant to restore the density of hair in their heads.
4. Addressing Underlying Conditions: Address any illnesses affecting hair growth such as thyroid problems, or lack of nutrients such as vitamin D.
5. Lifestyle Modifications: Learning to work on stress levels, dieting, or cutting on the dos and don’ts of hair is vital when combating hair loss as one would find out.
It is thus important to know when hair loss could be a sign of something else. Any abrupt, blurred, or unpredictable hair loss, or if the amount exceeds normal is especially advised to seek a dermatologist or a trichologist. It also reveals that if the hair loss issue is addressed before exacerbation, the chance to get back hair will increase.
It is crucial to distinguish between hair shedding and hair loss to treat the concerned problem correctly. Though shedding is completely normal for a human being and is determined by the hair growth cycle, hair loss may be more involved and may need professional help. As such, the causes of the indicators recognized can be treated to ensure no influence is left on hair health or appropriate treatment is sought when indicated.
Can Allergies Make You Cough? Allergy is one of the most widespread diseases or conditions…
Which Vitamin Deficiency Results in Hair Loss? This is a problem that people of all…
Can Gas Cause Back Pain? Sometimes, it is not easy to determine the cause of the…
Can Muscle Knots Cause Wrist Pain? Some of the main causes of pain include muscles…
Can You Drink Alcohol While Taking Steroids? This question of alcohol consumption and steroids is…
Can Allergies Make You Cough? Coughing is a normal physiological response that makes use of…